B.C. researchers uncover mechanism that keeps large whales from drowning while feeding on krill
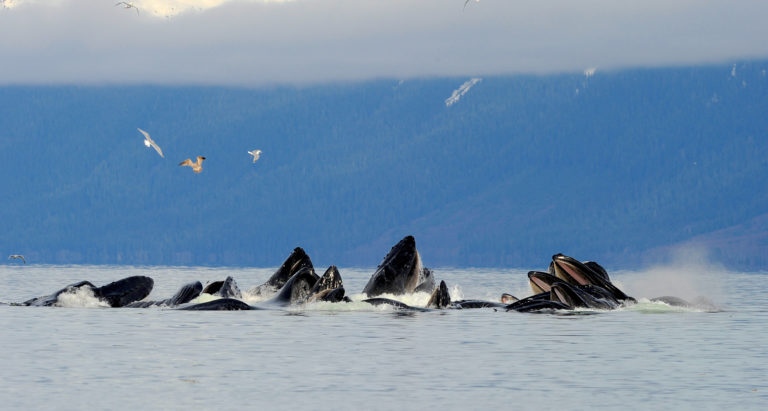 A group of humpback whales in Alaska, near Sitka. (UBC handout photo/Ari Friedlaender)
A group of humpback whales in Alaska, near Sitka. (UBC handout photo/Ari Friedlaender)
New research from the University of British Columbia is shedding light on the ways that whales feed underwater without flooding their airways with seawater.
The research, published this month in Current Biology, shows that lunge-feeding whales – the type that lunge and gulp at large schools of krill – have a special mechanism in the back of their mouths that stops water from entering their lungs when eating.
“It’s kind of like when a human’s uvula moves backwards to block our nasal passages, and our windpipe closes up while swallowing food,” says lead author Dr. Kelsey Gil, a postdoctoral researcher in the department of zoology, in a statement.
Specifically, a fleshy bulb acts as a plug, to close off upper airways, while a larynx closes to block lower airways.
The humpback whale and the blue whale are both lunge-feeders, but the scientists’ research focused on fin whales, thanks in part to being able to travel to Iceland in 2018 and examine carcass remains at a commercial whaling station.
“We haven’t seen this protective mechanism in any other animals, or in the literature. A lot of our knowledge about whales and dolphins comes from toothed whales, which have completely separated respiratory tracts, so similar assumptions have been made about lunge-feeding whales,” Gil said.
Lunge-feeders are impressive, Gil said, because sometimes the amount of food and water they consume is larger than their bodies. After snapping at krill, and while blocking the water from their airways, the whales then drain the ocean water through their baleen, leaving behind the tasty fish.
The study’s senior author Dr. Robert Shadwick, a professor in the UBC department of zoology, says the efficiency of the whales’ feeding is a key factor in their evolution.
“Bulk filter-feeding on krill swarms is highly efficient and the only way to provide the massive amount of energy needed to support such a large body size. This would not be possible without the special anatomical features we have described,” he said in a statement.
CTVNews.ca Top Stories

NDP calls out Conservatives for effort to squash pharmacare legislation
The federal New Democrats are calling out Conservative Leader Pierre Poilievre and his party for trying to block the bill that could pave the way for millions of Canadians to access birth control and diabetes coverage.
Stamp prices rise for the third time in five years amid financial woes for Canada Post
Canada Post is increasing stamp prices for the third time since 2019, a move the Crown corporation says is a "reality" of its sales-based revenue structure.
Winnipeg man admits to killing four women, argues he's not criminally responsible
Defence lawyers of Jeremy Skibicki have admitted in court the accused killed four Indigenous women, but argues he is not criminally responsible for the deaths by way of mental disorder – this latest development has triggered a judge-alone trial rather than a jury trial.
An El Nino-less summer is coming. Here's what that could mean for Canada
As Canadians brace themselves for summer temperatures, forecasters say a weakening El Nino cycle doesn’t mean relief from the heat.
Mediterranean staple may lower your risk of death from dementia, study finds
A daily spoonful of olive oil could lower your risk of dying from dementia, according to a new study by Harvard scientists.
A subset of Alzheimer's cases may be caused by two copies of a single gene, new research shows
For the first time, researchers have identified a genetic form of late-in-life Alzheimer’s disease — in people who inherit two copies of a worrisome gene.
Ontario MPP asked again to leave Ontario legislature over keffiyeh, Speaker loosens ban
An Ontario MPP was asked again to leave the Ontario legislature on Monday for wearing a keffiyeh, a garment that was banned by the Speaker last month due to its political symbolism.
WATCH Avian flu: Risk to humans grows as outbreaks spread, warns expert
H5N1 or avian flu is decimating wildlife around the world and is now spreading among cattle in the United States, sparking concerns about 'pandemic potential' for humans. Now a health expert is urging Canada to scale up surveillance north of the border.
Trudeau Liberals to unveil new bill Monday aimed at countering foreign interference
Democratic Institutions Minister Dominic LeBlanc will be tabling legislation on Monday aimed at countering foreign interference in Canada. Federal officials have scheduled a technical briefing on the incoming bill for Monday afternoon.