How a 'Band-Aid' urgent care strategy contributed to B.C.'s primary care crisis
The decision to focus on urgent and emergency health care to avert long waits played a key role in B.C.’s current primary care crisis, and the costlier care is compounding the problem.
That conclusion is widely agreed on by expert analysts as well as frontline physicians increasingly speaking out about their inability to continue to prop up the health-care system on an inadequate and antiquated pay system that’s seeing increasing numbers walk away from family practice.
CTV News asked one of Canada’s experts on health-care systems whether the government’s desire to avoid the negative optics and experience associated with hallway medicine and crowded hospital waiting rooms may have been a motivator in directing funding towards urgent care centres and hospitals.
“As a Band-Aid, when people are really struggling to access primary care, I guess it's understandable as a choice,” said Dalhousie associate professor of Family Medicine, Ruth Lavergne. “We've all experienced those waits in the emergency department, but as a solution this doesn’t fully address that issue and it has really deflected attention away from the real need for relationship-based primary care in the community.”
She also pointed out that hospital wait times are publicly posted and it’s easy to tabulate how many injuries or illnesses are handled, but the care that family doctors and nurse practitioners provide upstream in the medical system prevent more serious disease and worsening of symptoms, which is difficult to quantify.
“It's true it's harder to measure and it's not a quick fix to try to build a more robust primary care system and I think that's kind of what got us into this mess,” said Lavergne. “This is a problem many years in the making.”
EARLY INTERVENTION MORE EFFECTIVE, CHEAPER
Until now, focussing on tackling the more obvious, visible, signs of a strained health-care system made for good headlines, presenting the government as proactive and willing to try new things. But urgent care centers in particular have not provided the efficient emergency-department-avoiding service they government claimed they would.
“What's clear now is that despite significant investment, these centres have fallen short of meeting the population needs,” said long-time family physician, Dr. Kathleen Ross. “Without family doctors, British Columbians don't have access to that continuity of care and personal relationship that evidence repeatedly shows leads to better outcomes and, perhaps important to society, lower overall costs to achieve those better outcomes.”
She says that a hospital visit costs much more than a visit to a primary care provider, but with physicians trained in family medicine opting to practice in hospitals or other settings rather than run their own business for considerably less money -- the government has to act.
“Health-care systems are complex and certainly challenging to change overnight,” Ross acknowledged. “But there’s no question now that we're in a crisis of access to doctors in British Columbia and the government will need to work quickly to doctor to address the crisis.”
THE HEALTH MINISTER RESPONDS
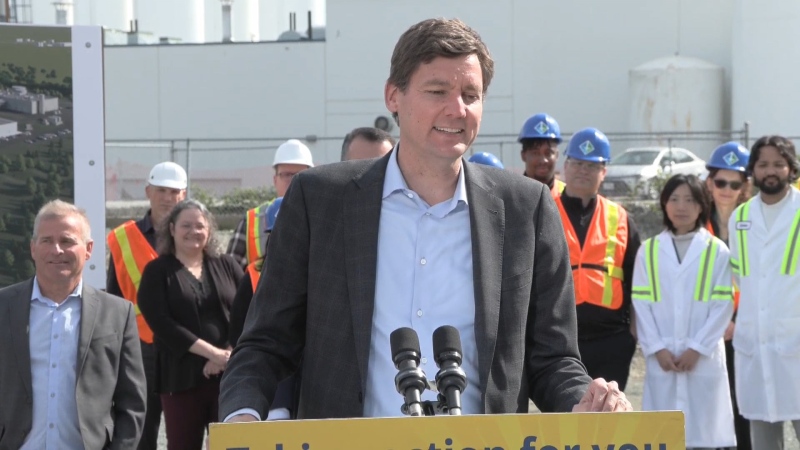
The health minister, who was the subject of a rare public rebuke by a doctors’ association two weeks earlier, addressed the question of priorities when asked by CTV News on Wednesday.
"I absolutely agree with you about the central role in primary care in the health-care system, its role in prevention but also it's role of navigating people in the system," said Adrian Dix.
But he defended his government’s record in supporting the establishment of 59 primary care networks in the province, as well as 27 Urgent and Primary Care Centres, though his ministry will not provide full details on how many patients are seen on an urgent or ongoing, longitudinal basis.
“I don't think there's even the slightest bit of doubt about this, that we've given more priority to primary care than any other government in the history of British Columbia," Dix claimed.
But that pronouncement is at odds with what the premier has acknowledged is “a crisis” with some one million British Columbians without a primary care provider, and veteran frontline medical personnel who say they’ve never seen the system in such rough shape.
While Dix emphasized the impacts of the pandemic, Ross characterized it as a “last straw” situation.
“Physicians have literally been carrying the primary care system for decades, paying a personal ‘passion tax’ by continuing to subsidize the cost of running a practice and ensuring their patients receive the care that they need,” she said. “Physicians are telling us it's simply no longer possible for them to compensate.”
CTVNews.ca Top Stories

Bodies found by U.S. authorities searching for missing B.C. kayakers
United States authorities who have been searching for a pair of missing kayakers from British Columbia since the weekend have recovered two bodies in the nearby San Juan Islands of Washington state.
Amid concerns over 'collateral damage' Trudeau, Freeland defend capital gains tax change
Facing pushback from physicians and businesspeople over the coming increase to the capital gains inclusion rate, Prime Minister Justin Trudeau and his deputy Chrystia Freeland are standing by their plan to target Canada's highest earners.
'It's discriminatory': Individuals refused entry to Ontario legislature for wearing keffiyeh
Individuals being barred from entering Ontario’s legislature while wearing a keffiyeh say the garment is part of their cultural identity— and the only ones making it political are the politicians banning it.
Tom Mulcair: Park littered with trash after 'pilot project' is perfect symbol of Trudeau governance
Former NDP leader Tom Mulcair says that what's happening now in a trash-littered federal park in Quebec is a perfect metaphor for how the Trudeau government runs things.
Saskatchewan households will continue to receive carbon tax rebate: Trudeau
Households in Saskatchewan will continue to receive Canada Carbon Rebate payments, despite the province refusing to remit the federal carbon price on natural gas, Prime Minister Justin Trudeau said Tuesday.
'It's just so hard to let it go': Umar Zameer still haunted by death of Toronto police officer
'We hoped for this day, but we were scared that it would not never ever come because it took so long.' That’s what Umar Zameer, the man recently acquitted in the death of a Toronto police officer, told CTV News Toronto in a sit-down interview on Tuesday.
Senate expenses climbed to $7.2 million in 2023, up nearly 30%
Senators in Canada claimed $7.2 million in expenses in 2023, a nearly 30 per cent increase over the previous year.
Canucks goalie Thatcher Demko won't play in Game 2
The Vancouver Canucks will be without all-star goalie Thatcher Demko when they face the Nashville Predators in Game 2 of their first-round playoff series.
Pedestrian, baby injured after stroller struck and dragged by vehicle in Squamish, B.C.
Police say a baby and a pedestrian suffered non-life-threatening injuries after a vehicle struck a baby stroller and dragged it for two blocks before stopping in Squamish, B.C.