Fight against toxic mining runoff from Canada persists, say U.S. Indigenous leaders
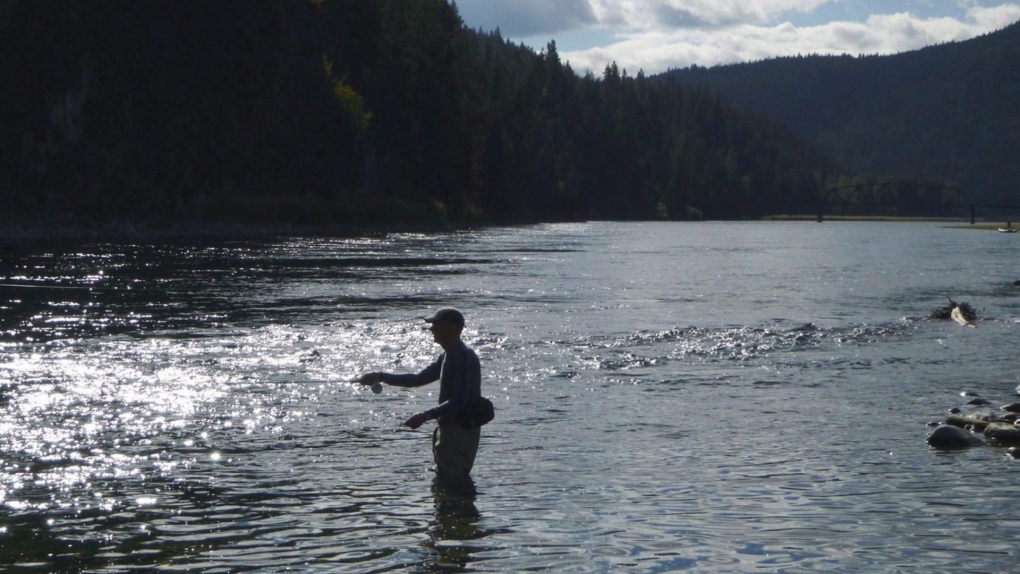 A fly fisherman casts on the Kootenai River, downstream of the Koocanusa Reservoir at the centre of the dispute, near the Montana-Idaho border and Leonia, Idaho, on Sept. 19, 2014. U.S. Indigenous leaders say they aren’t about to stop pushing Canada to agree to a bilateral investigation into toxing mining runoff from B.C. THE CANADIAN PRESS/AP - The Spokesman Review, Rich Landers
A fly fisherman casts on the Kootenai River, downstream of the Koocanusa Reservoir at the centre of the dispute, near the Montana-Idaho border and Leonia, Idaho, on Sept. 19, 2014. U.S. Indigenous leaders say they aren’t about to stop pushing Canada to agree to a bilateral investigation into toxing mining runoff from B.C. THE CANADIAN PRESS/AP - The Spokesman Review, Rich Landers
U.S. Indigenous leaders from the Pacific Northwest say they won't give up trying to convince Canada's federal government to agree to a bilateral investigation of toxic mining runoff from the B.C. Interior.
Representatives from several U.S. tribes were in D.C. Tuesday and Wednesday to meet with officials from the White House, the State Department and the Department of the Interior, as well as with lawmakers on Capitol Hill.
Their cause is the same as it was 11 years ago: a bilateral investigation under the 1909 Boundary Waters Treaty into mining pollution from B.C. that they say is poisoning the waters of a vital cross-border watershed.
Communities in B.C., Washington state, Idaho and Montana have been contending for more than a decade with selenium and other toxins leaching into their watershed from coal mining operations in the province's Elk Valley.
“I'm just afraid of studying this to death. Our river is dying,” said Gary Aitken Jr., vice-president of the Kootenai Tribe of Idaho, after a series of meetings Wednesday with U.S. officials.
On Friday, President Joe Biden and Prime Minister Justin Trudeau promised a tentative agreement by this summer on addressing the impact of pollution in the Elk-Kootenay watershed, which extends from B.C. through several U.S. states.
But they stopped short of what Canadian and U.S. conservationists and Indigenous leaders have been demanding for more than a decade: an investigation by the International Joint Commission, a bilateral panel established under the terms of the 1909 Boundary Waters Treaty.
Such an investigation, known in treaty parlance as a joint reference, requires both countries to agree. The U.S. has long pledged its support for the idea, but Canada has been dragging its heels for years.
Friday's announcement was a sign of progress, Aitken acknowledged. But he said it also showed that their fight is not over.
“I don't want to study more, study more - we've done enough with the studies. We know what's going on. I don't want to keep that going and watch our river die.”
In their joint statement Friday, Biden and Trudeau said Canada and the U.S. would work toward “an agreement in principle by this summer to reduce and mitigate the impacts of water pollution in the Elk-Kootenay watershed.”
Any forthcoming agreement on pollution from B.C.'s Elk Valley would be in partnership with tribes and Indigenous Peoples from both countries, and would aim to “protect the people and species that depend on this vital river system,” it said.
The principal mining player in the region, Teck Resources, has already spent more than $1.2 billion in an effort to fix the problem, with plans for $750 million more over the next two years.
The company's strategy includes the Elk Valley Water Quality Plan, developed with help from Indigenous stakeholders, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, the state government in Montana, the B.C. government and Ottawa.
Teck calls the plan “among the largest and most collaborative water quality management and monitoring programs in the world.” Separate water treatment and mitigation efforts have already proven effective, the company adds.
But Indigenous leaders say selenium levels in the water are still too high.
Last summer, following similar meetings with several U.S. tribes, the State Department reaffirmed its own support for a reference to investigate the transboundary impact of Canadian mining in the region.
Billy Barquin, the Kootenai tribe's attorney general, said State continues to back the group's efforts to get the International Joint Commission involved.
“Everything's still on the table,” Barquin said. “We'll continue to pressure both the U.S. and Canadian governments to accept an IJC reference.”
The commission is scheduled to meet next month in D.C., and Barquin said the Kootenai Tribe and others may send a delegation back to the U.S. capital “to be outside the room.”
The goal there, he said, would be “to keep on reminding both national governments that this is a significant issue for the nation that needs to be addressed.”
Taking the matter to court also remains an option, Barquin added.
“Ideally, it's a joint reference - both countries agree to co-operate and do the right thing,” he said.
“But if that doesn't happen, there are a number of other options that we in the nation are exploring, whether it's through different legislation, more lobbying or litigation.”
The watershed lies within the transboundary Columbia River basin, which has been the subject of ongoing treaty discussions since 2018. Biden and Trudeau also promised to make progress on those efforts, which are focused on new rules for flood risk management, power generation and shared environmental benefits.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published March 29, 2023.
CTVNews.ca Top Stories

Quebec nurse had to clean up after husband's death in Montreal hospital
On a night she should have been mourning, a nurse from Quebec's Laurentians region says she was forced to clean up her husband after he died at a hospital in Montreal.
'Anything to win': Trudeau says as Poilievre defends meeting protesters
Prime Minister Justin Trudeau is accusing Conservative Leader Pierre Poilievre of welcoming 'the support of conspiracy theorists and extremists,' after the Conservative leader was photographed meeting with protesters, which his office has defended.
'My stomach dropped': Winnipeg man speaks out after being criminally harassed following single online date
A Winnipeg man said a single date gone wrong led to years of criminal harassment, false arrests, stress and depression.
What is changing about Canada's capital gains tax and how does it impact me?
The federal government's proposed change to capital gains taxation is expected to increase taxes on investments and mainly affect wealthy Canadians and businesses. Here's what you need to know about the move.
Bank of Canada officials split on when to start cutting interest rates
Members of the Bank of Canada's governing council were split on how long the central bank should wait before it starts cutting interest rates when they met earlier this month.
Pilot reported fire onboard plane carrying fuel, attempted to return to Fairbanks just before crash
One of the two pilots aboard an airplane carrying fuel reported there was a fire on the airplane shortly before it crashed and burned outside Fairbanks, killing both people on board, a federal aviation official said Wednesday.
Police tangle with students in Texas and California as wave of campus protest against Gaza war grows
Police tangled with student demonstrators in Texas and California while new encampments sprouted Wednesday at Harvard and other colleges as school leaders sought ways to defuse a growing wave of pro-Palestinian protests.
'One of the single most terrifying things ever': Ontario couple among passengers on sinking tour boat in Dominican Republic
A Toronto couple are speaking out about their 'extremely dangerous' experience on board a sinking tour boat in the Dominican Republic last week.
7 surveillance videos linked to extortions of South Asian home builders in Edmonton released
The Edmonton Police Service has released a number of surveillance videos related to a series of extortion cases in the city now dubbed 'Project Gaslight.'